Trends change quickly, but the marketing fundamentals stay the same. There are always new technologies, channels, and buzzwords coming out. However, the companies that keep expanding are the ones that know how to do things that never change. In 2025, businesses must deal with stricter privacy rules, increasing customer expectations, and AI. This guide to marketing fundamentals goes over the basics of marketing again, such as research, segmentation, content, channels, and measurement. It also contains new things, like putting privacy first regarding data and leveraging AI.
Readers will learn how the basics are connected to growth approaches and leave with a viable plan for implementing what they learned. The debate’s central premise is that companies can expand in a way that lasts if they use good basics and the latest tools.
Why Focus on Marketing Fundamentals in 2025
In 2025, concentrate on the basics. It sounds like the business world is louder than ever in 2025. AI tools can now produce text, make visuals, and even figure out what clients want. At the same time, legislation like GDPR updates, California’s CPRA, and other privacy-first rules around the world are changing how data is utilized.
Marketers often feel they must chase every new tool or platform because customer behaviour changes quickly. However, Adweek and Forbes say that following trends doesn’t usually make you stronger. Fundamentals make it easier to understand, save money, and improve attribution. Businesses that use tried-and-true marketing techniques can adjust more swiftly as new tools emerge. They know what to look for, how to evaluate performance, and what to do to boost sales. Principles help you better understand your customers, spend your budgets, and deliver better stories. That’s why innovative leaders in 2025 are going back to the basics and adding modern ways to do things on top of them.
Core Marketing Principles — A Quick Taxonomy
It can be hard to grasp marketing, but the essentials are easy to get. It is the right way for every solid strategy:
- Getting to know your customers,
- Plan,
- Setting Up Offer (price and product), Ways,
- Creative execution, and
- How to measure.
The first thing to consider is always the company’s goal, whether getting new customers, keeping old ones, or making more money. Once teams know what they want, they can move through the processes and pick the right tools and methods.
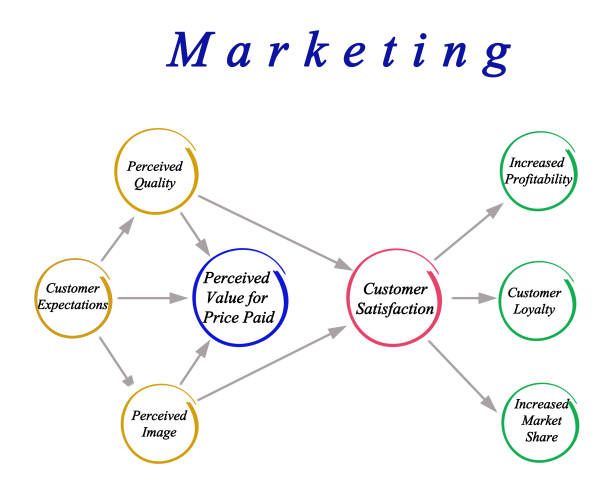
Market Research & Insight: The Foundation

The Basis of Market Research and Insight Knowledge, not gut feelings, is the first step to good marketing. With market research, you have the evidence you need to make every choice after that. Primary research methods like interviews, focus groups, and surveys give you new, first-hand knowledge about people’s desires. Secondary research already employs information, like publications, industry studies, competitive intelligence, or analytics data. Both are really significant.
Companies performing well use systematic methods like the jobs-to-be-done framework to determine what their customers want to do or detailed personas to determine what drives and stops them. A simple technique works well:
- Make queries like “Why do prospects leave?” and “What makes them buy?”
- Surveys, CRM exports, or social listening are all good ways to get insight.
- Get ideas on themes together.
- Put the outcomes that best fit your business goals at the top of your list.
Professionals can make the process more official and turn raw data into strategies that can be put into action with the help of tools like the HubSpot market research templates.
Guide to marketing fundamentals:Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning
Segmentation helps businesses classify customers based on things they have in common. The best standards are:
- Behavioral (how often you buy something and how often you use it).
- Attitudinal (likes, values, and priorities).
- Demographics, such as age, income, and level of education.
- Firmographic (the size of the business, the field, and the area).
After you know your sectors, you must find out how big the market is. Businesses usually make a TAM (total addressable market), a SAM (serviceable addressable market), and a SOM (share of market) before they figure out their ideal customer profile (ICP). Then, positioning shows how the brand fits into the customer’s life. A standard formula is:
Our [product/service] is the [category] that [benefit] for [target segment] because [reason to believe].
Positioning statements make it obvious what path future campaigns should take. Testimonials, ROI numbers, and case studies are proof points that make the claim convincing.
Guide to marketing fundamentals: The 7 Ps Applied

The “7 Ps of marketing” will still be significant in 2025, just like when they were first developed. Here are some modern ways they could be used:
- Product: SaaS tools with free and premium levels.
- Price: A subscription model with several degrees of value.
- Place: Available through many different channels, such as e-commerce and retail.
- Promotion: Campaigns that use a mix of free and paid ads across several platforms.
- People: Customer service teams affect how long consumers stay. Onboarding flows that make it easier for users to utilise are part of the process.
- Physical Evidence: Reviews and case studies are two types of social proof. There is a measurable result for each “P.” For instance, pricing affects lifetime value (LTV) and turnover, while process affects net promoter score (NPS).
- Planning: the Customer Journey and Experience, People don’t usually buy something after only one interaction. Instead, they move through a sequence of steps: discover, appraise, buy, onboard, and advocate.
Customer Journey & Experience Design
- Discover: Learn about ads, SEO, and material that shows you are a thinking leader.
- Evaluate: Look at product demos, reviews, and guides that compare different products.
- Buy: Prices are transparent, and checkout is easy.
- Onboarding: training, welcome emails, and help with the program.
- Advocate: programs that reward loyalty, recommendations, and building a community. Retention loops are pretty significant.
A well-thought-out onboarding process can make people more likely to stay and less likely to leave. Figuring out where things go wrong at each level helps things run more smoothly and generates stronger loyalty.
Channels—Rules and Choosing at a High Level.
You must be diligent in picking the proper channels. A channel fit framework looks at three things:
- Audience: Who are you trying to reach?
- Intent: Where do they spend their free time? What are they doing (researching, buying, or browsing around)?
- Budget/measurement: Can you reach your goals and determine how much money you’ll make?
Marketers frequently find a middle ground
Blogs, websites, and newsletters, examples of owned media. PR coverage, social shares, and influencer mentions are examples of earned media. Paid media includes adverts on social media, search engines, and programmatic TV. Further, test a few things and then grow the ones that work. Businesses shouldn’t try to do too much with 10 channels. Instead, they should choose and work on two or three that best fit their ICP.
Content Strategy & SEO
Today, content is the most crucial part of marketing. A successful strategy starts with a content purpose that informs you what problem your audience has, what formats to employ, and how to get the information out there. In 2025, the idea of a pillar page and subject cluster is still very relevant. A core page talks about a big idea, like “marketing fundamentals,” while supplemental articles talk about smaller ideas, like “segmentation basics” or “customer journey mapping.” Linking to other pages on your site makes it more trustworthy and helps it rank better in search results. It’s really crucial to connect information to what consumers want.
People require instructional guides when they ask for information. People need comparison tables or demos when they ask for transactions. You also have to utilise the duplicate content again. A webinar becomes a blog post, a LinkedIn carousel, and a short film. It spreads the word without having to start from scratch. Businesses use analytics like time on site, scroll depth, lead capture, and conversions to see how things are going. Neil Patel’s content guides and other materials give you much tactical information.
Paid and Performance Marketing

Performance marketing is still a good way to gain new customers. The main groups are: Search adverts for those who are very interested in what you have to say. Ads on social media to get people to know your business and find people who look like you. Programmatic display for a big audience. Retargeting to attract leads that are already interested. The fundamental goal of a bid strategy should be conversions, not impressions. Marketers need to evaluate the cost of gaining new customers (CAC) to the value of those consumers over their whole lifetimes (LTV). If a campaign can’t keep its CAC/LTV ratios consistent, it should be cut or altered.
Email, CRM & Retention Marketing
Email is still one of the finest ways to make money with digital marketing. Onboarding, engagement, and renewal efforts, divided into segments, are some modern strategies to keep consumers.
Trigger-based flows happen when someone leaves a cart or meets a goal while using a product—campaigns to regain users who haven’t used the service.
When used with CRM data, email allows you a direct, owned means to connect with people. Social media marketing platforms are becoming locations where people may observe and chat with each other. Companies need to know the distinction between community and places where consumers may talk to each other. For example , private LinkedIn groups, Discord, and Slack groups.
Broadcast: Public-facing channels for reach (Instagram, TikTok, X).
Broadcast: Public channels like Instagram, TikTok, and X that people may use to talk to each other. When influencer marketing is founded on honesty, it works best. Younger people trust user-generated content (UGC) more than well-polished commercials.
Measurement, KPIs & Experimentation
You have to be very careful when measuring things to grow in a way that lasts. Companies should pick a “north star” metric, like monthly recurring income, and then use channel-level KPIs to support it. Attribution models are very significant. Last-click attribution is too easy; data-driven models better demonstrate how individuals travel through several touches. There should be a clear plan for regular tests, such as A/B tests of creativity, messages, or offers. The most important thing is to keep your analytics clean. You must employ consistent labelling, an organised event taxonomy, and cohort monitoring to gain relevant information.
Modern Shifts to Incorporate into Marketing Fundamentals
AI Acceleration
Artificial intelligence makes it faster to make things, split audiences, and make things more personal. Marketers use AI to write ads, make graphics, and even forecast how likely someone is to leave. But you should be careful. If you rely on it too much, the brand voice can get weaker, or the facts might be wrong. The greatest teams don’t think of AI as an autopilot but as a co-pilot.
Privacy-First Marketing
The time has come for a world without cookies. Browsers no longer support third-party cookies, so businesses have to acquire first-party data, including email addresses, app usage, and preference centres. Techniques like hashed IDs and consent-based tracking are what make privacy-first personalisation possible.
Practical Rule
Rule in Action: Long-term personalisation power comes from having solid data and getting explicit permission. A company that respects privacy while giving customers valuable information builds confidence and keeps them as customers.
Competitor Snapshot — What Top Resources Emphasize
- HubSpot: Offers organised templates, inbound frameworks, and playbooks about CRM. Very helpful for businesses of all sizes.
- Neil Patel: He teaches you SEO and content tips that will help you acquire many more visits.
- Brafton: It brings new ideas and explains the 7 Ps. Forbes and
- Adweek: Look at big-picture trends and strategic insights that could help you make bigger investments. The ideal way to do this is to combine these points of view: use HubSpot for process, Patel for traffic execution, and Adweek for strategic framing.
Actionable Framework & Checklist
Any business can use a short checklist to get the essentials done:
- Set a goal for the business and a north star metric.
- Do three interviews with customers and one in-depth look at the data.
- Write an ICP and a statement of your position.
- Pick three channels: one you own, one you earned, and one you paid for.
- Make a plan for your content that includes both pillar and cluster parts.
- Within 30 days, start two tests. Set up cohort analysis and event tracking.
- Get authorisation and a first-party email. At least one effort should be made to keep people.
- Look at your plan once a month. A 14-day marketing sprint gets things going: Planning and research in the first week. Week 2: Create, test, and measure.
Final words
In the end, People who keep to the essentials and add modern execution to their marketing fundamentals in 2025 will be rewarded. AI, privacy, and personalisation change how we do things, but the basic ideas of growth—insight, positioning, content, channels, and measurement—stay the same. You may read the whole guide to marketing fundamentals twice for better understanding. You can’t overlook the basics; they’re what make growth last.
FAQs
1. What are marketing fundamentals?
Research, segmentation, positioning, the 7 Ps, channel strategy, content, and measurement are the main ideas underlying excellent marketing.
2. Why are marketing fundamentals more important than trends in 2025?
Fundamentals give things a sense of stability because privacy rules and AI technology change constantly. They assist firms in thinking about fresh ideas from the point of view of what customers say and what can be measured.
3. How does first-party data fit into marketing fundamentals?
Instead of third-party cookies, first-party data is permitted to personalise and keep customers.
4. What is the most effective marketing channel in 2025?
Not every channel works for everyone. Your audience’s behaviour, goals, and money determine the best channel for you. A lot of businesses employ their own content, email, and sponsored ads all at the same time.
5. How should small businesses apply these principles?
Make a clear ICP and a short content strategy, choose two or three channels, and watch one essential number. Make sure you study and are consistent before you grow.